- Evaporative cooling, like sweating, might cut back vitality use in knowledge facilities
- New fiber membrane handles warmth with zero added vitality use
- Researchers retool filtration materials to chill electronics passively
As AI and cloud computing develop, the rising demand for knowledge processing is driving up warmth output, with cooling already making up almost 40% of an information heart's vitality use and projected to greater than double worldwide by 2030.
Researchers on the College of California San Diego have developed a brand new cooling know-how that mimics the way in which animals regulate physique temperature… by sweating.
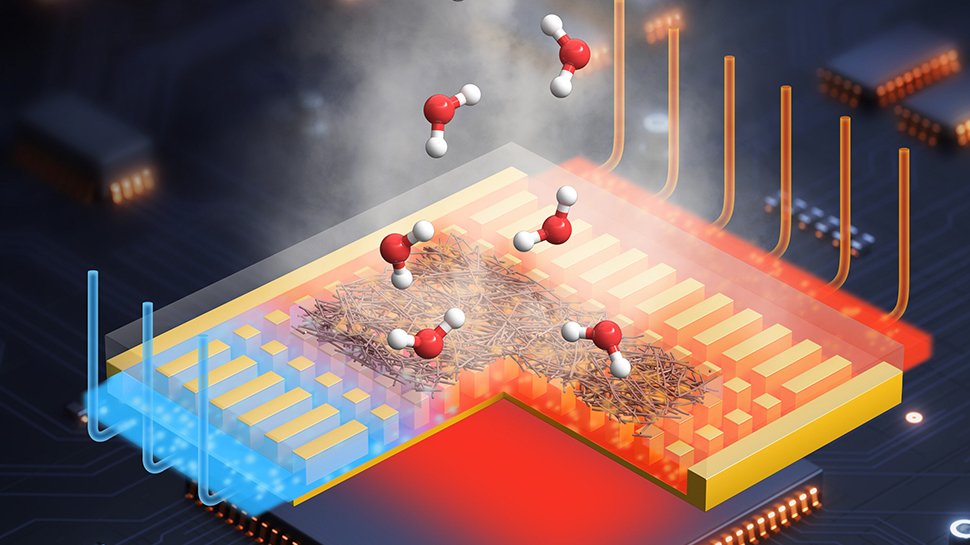
The passive system removes warmth from electronics utilizing evaporation, providing a possible different to conventional cooling strategies in knowledge facilities and different high-powered computing environments.
Discovering the “candy spot”
The core of the system is a fiber membrane with a community of tiny, interconnected pores that use capillary motion to attract cooling liquid throughout the floor.
Because the liquid evaporates, it effectively removes warmth with out requiring further vitality.
“In comparison with conventional air or liquid cooling, evaporation can dissipate greater warmth flux whereas utilizing much less vitality,” mentioned Renkun Chen, a professor within the Division of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at UC San Diego. Chen co-led the challenge with professors Shengqiang Cai and Abhishek Saha.
The analysis was revealed within the journal Joule, explaining how Chen’s group, together with Ph.D. pupil Tianshi Feng and postdoctoral researcher Yu Pei, examined the membrane below variable warmth circumstances.
Signal as much as the TechRadar Professional e-newsletter to get all the highest information, opinion, options and steerage your small business must succeed!
It dealt with over 800 watts per sq. centimeter of warmth, a document for the sort of cooling system. It additionally carried out persistently over a number of hours.
Conventional porous membranes have typically failed because of clogging or boiling. Chen defined that the group discovered a “candy spot” with the membrane’s pore measurement and construction.
“These fiber membranes had been initially designed for filtration, and nobody had beforehand explored their use in evaporation," mentioned Chen. "We acknowledged that their distinctive structural traits – interconnected pores and simply the best pore measurement – might make them superb for environment friendly evaporative cooling. What stunned us was that, with the best mechanical reinforcement, they not solely withstood the excessive warmth flux–they carried out extraordinarily nicely below it.”
The researchers consider the membrane remains to be working beneath its full potential.
They’re now refining the design and dealing on methods to combine it into chilly plates, flat gadgets used to chill chips like CPUs and GPUs.
The group can also be making ready to commercialize the know-how by a startup. Their aim is to offer scalable, low-energy cooling options as world knowledge demand continues to develop.
By way of Tech Xplore
You may additionally like
- One among world's largest oil firms simply launched a singular cooling fluid for knowledge facilities and AI chips
- I sat down with two cooling specialists to seek out out what AI's largest drawback is within the knowledge heart
- Cooling high-density knowledge facilities with coolant distribution items